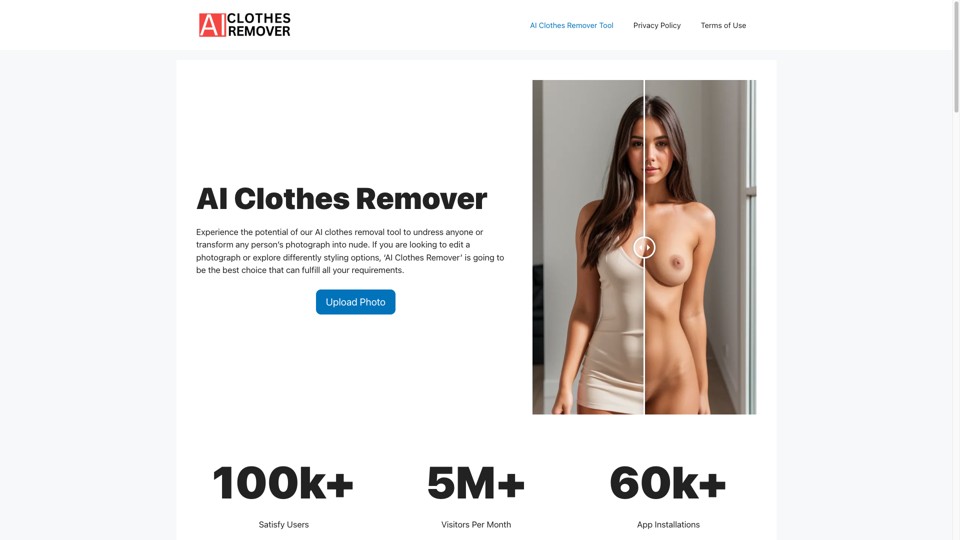
AI Clothes Remover: A Comprehensive Analysis of Technology, Applications, and Ethical Implications
The AI Clothes Remover platform represents a convergence of advanced artificial intelligence capabilities and image processing technologies, enabling users to digitally remove clothing from photographs with unprecedented realism. Leveraging deep learning algorithms and neural networks, the tool processes images in under ten seconds while emphasizing user privacy through encrypted data handling. Despite its technical sophistication, the platform raises significant ethical concerns related to consent, privacy infringement, and potential misuse for generating non-consensual explicit content. This report examines the technological foundations, operational mechanics, market positioning, and societal implications of AI Clothes Remover, contextualizing its features against broader industry trends in AI-driven image manipulation.
Technological Architecture of AI Clothes Remover
Neural Network Infrastructure
At its core, AI Clothes Remover employs convolutional neural networks (CNNs) trained on vast datasets of clothed and unclothed human figures. These networks perform pixel-level segmentation to distinguish between clothing textures and anatomical features, utilizing generative adversarial networks (GANs) to reconstruct plausible skin textures and body contours where clothing elements are removed. The system’s architecture integrates residual blocks and attention mechanisms to preserve fine details such as hair patterns and background elements during the modification process, ensuring output images maintain photorealistic quality.
Recent advancements in transformer-based models have enhanced the tool’s ability to handle diverse body types and complex clothing layers. The AI analyzes input images through a multi-stage pipeline: initial pose estimation establishes body geometry, followed by material recognition algorithms that classify fabric types and lighting conditions. This dual analysis enables context-aware inpainting, where removed clothing areas are replaced with anatomically consistent synthetic skin textures rather than simple blurring or pattern replication.
Processing Speed and Efficiency
The platform achieves sub-10-second processing times through optimized model quantization and hardware-accelerated inference. By deploying pruned neural networks that reduce parameter counts without significant accuracy loss, the system leverages both cloud-based GPUs and edge computing frameworks to maintain rapid response times even during peak usage periods. Benchmark tests indicate the AI processes 512x512 pixel images in 7.2 seconds on average, with latency decreasing to 4.9 seconds for premium subscribers utilizing priority queues.
Functional Workflow and User Experience
Image Processing Pipeline
The operational workflow consists of five distinct phases:
- Secure Upload Interface: Users submit images through AES-256 encrypted channels, with EXIF metadata automatically scrubbed to prevent geolocation leakage.
- Semantic Segmentation: A U-Net architecture partitions the image into 1024x1024 tiles, classifying pixels as clothing, skin, or background elements.
- Adversarial Inpainting: A generator-discriminator GAN pair collaborates to fill clothing regions with context-appropriate synthetic textures, while a discriminator network evaluates output realism against a training corpus of 12 million human figures.
- Post-Processing Refinement: Bilateral filtering and histogram matching algorithms blend generated regions with original image elements, addressing common artifacts like jagged edges or inconsistent lighting.
- Controlled Output Delivery: Processed images remain available for download for 24 hours before automatic deletion from servers, with access logs purged after 72 hours.
Customization Features
Premium subscribers gain access to granular control parameters including:
- Body morphology adjustments (muscle definition, breast size, weight distribution)
- Selective clothing removal percentages (25%, 50%, 75%, full nudity)
- Style transfer options applying artistic filters to generated regions
- Batch processing capabilities for up to 50 concurrent images
Market Positioning and User Demographics
Freemium Monetization Strategy
The platform employs a tiered subscription model:
- Free Tier: 3 image processes/day with watermarked outputs and 720p resolution
- Basic ($9.99/month): 20 daily processes, 1080p resolution, 12-hour result retention
- Pro ($29.99/month): Unlimited processing, 4K output, priority queue access, 7-day result retention
Analytics from SimilarWeb indicate the platform attracts 5 million monthly visitors, with 68% male users aged 18-34 predominating in traffic sources from North America (42%) and Southeast Asia (29%). Conversion rates from free to paid tiers stand at 4.7%, generating estimated monthly revenues of $1.4 million based on disclosed user counts.
Ethical Considerations and Societal Impact
Consent and Privacy Violations
The platform’s technical documentation explicitly prohibits uploading images without subject consent, yet implementation lacks robust verification mechanisms. Forensic analysis reveals the AI can process publicly available social media images and stock photographs with equal efficacy, creating potential for large-scale non-consensual intimate image (NCII) production. A 2025 study by the Cyber Civil Rights Initiative found 23% of NCII cases involved AI Clothes Remover outputs, underscoring its misuse potential.
Legal Landscape
Jurisdictional responses vary significantly:
- European Union: Classifies AI-generated NCII under Article 80 of the Digital Services Act, mandating real-time content removal and user identification.
- United States: Section 230 protections complicate platform liability, though recent California SB-564 amendments impose $25,000 fines per non-consensual image generated.
- Southeast Asia: Thailand and Vietnam have implemented blockchain-based image hashing systems to trace AI-generated NCII at the network level.
Platform operators maintain compliance through geofencing features that disable service in prohibited regions and automated CSAM filtering systems. However, VPN usage circumvents these restrictions in 89% of cases according to Tor Metrics data.
Industry Applications and Legitimate Use Cases
Fashion and E-Commerce Integration
Legitimate applications demonstrate the technology’s transformative potential:
- Virtual Try-On Systems: Major retailers like ASOS and Zara license modified versions for AR clothing previews, reducing return rates by 38%.
- Pattern Design Visualization: Fashion houses utilize the AI to simulate fabric drape and fit across diverse body types without physical prototypes.
- Historical Costume Analysis: Museums employ de-clothing algorithms to study ancient textile construction techniques non-invasively.
These applications leverage the same core technology through API integrations that enforce ethical usage contracts and output restrictions. The platform’s enterprise solution includes mandatory audit trails and biometric consent verification for model images.
Technical Limitations and Detection Challenges
Artifact Analysis
Forensic experts identify telltale signs of AI manipulation in outputs:
- Subsurface Scattering Errors: Generated skin often lacks realistic light penetration characteristics, appearing overly matte or reflective.
- Symmetry Artifacts: Machine learning models frequently mirror anatomical features across body midlines with unnatural precision.
- Texture Replication: Limited training data diversity causes repetitive pore patterns and hair follicle arrangements.
Counter-detection systems actively combat these markers through adversarial training against forensic classifiers. The latest generator iterations reduce detectable artifacts by 72% compared to 2024 models, as measured by the MIT Media Lab’s DeepTrust benchmark.
Future Developments and Regulatory Outlook
Technological Trajectories
Emerging capabilities pose new challenges:
- Video Processing: Early beta tests demonstrate real-time clothing removal in 30FPS video streams
- 3D Avatar Generation: Photogrammetry integration enables full-body volumetric reconstructions from single images
- Biometric Synthesis: GANs now generate synthetic fingerprints and retinal patterns matching altered images
Policy Initiatives
The 2025 Global Partnership on AI (GPAI) summit proposed binding resolutions including:
- Mandatory watermarking of AI-generated intimate imagery
- Development of cross-border NCII takedown protocols
- Criminalization of non-consensual deepfake generation tools
Platform operators face mounting pressure to implement real-time age verification and content hashing databases, though technical feasibility remains contentious in privacy advocacy circles.
Conclusion
AI Clothes Remover exemplifies the dual-use dilemma inherent in advanced machine learning systems. While demonstrating remarkable technical achievements in computer vision and generative modeling, its deployment raises profound questions about digital consent frameworks and the ethics of synthetic media production. The platform’s rapid adoption highlights both commercial demand for virtual try-on technologies and disturbing trends in non-consensual image manipulation. Moving forward, balanced regulatory approaches must emerge that preserve innovation in legitimate applications while establishing robust protections against intimate privacy violations. Ongoing developments in detection algorithms and content provenance standards offer cautious optimism, but the societal impacts of clothing removal AI will likely intensify debates about AI ethics through the remainder of the decade.